
 Need sources for your literature review? Struggling to find sources for your assignment, research proposal or thesis?
Need sources for your literature review? Struggling to find sources for your assignment, research proposal or thesis?
The Library can assist with a literature search, which is a systematic and comprehensive search for published, academic material on your specific subject/topic. How do you request one? Simply go to Request a literature search .
If you are experiencing problems accessing the form, please use this link.

The subscription identifier icon ![]() indicates articles where you have access to full text.
indicates articles where you have access to full text.
The Advanced Keyword/Phrases tab on the Advanced Search Options page provides a structured way for you to perform a more complex search. Follow this procedure to perform an Advanced Search:
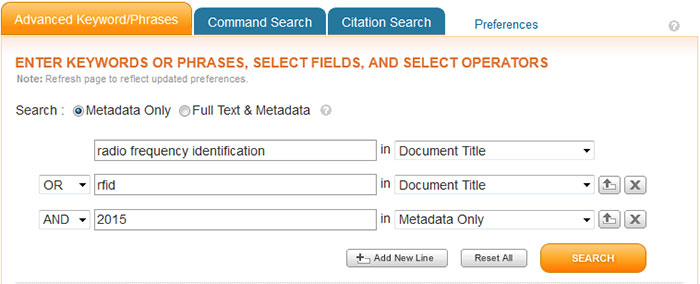
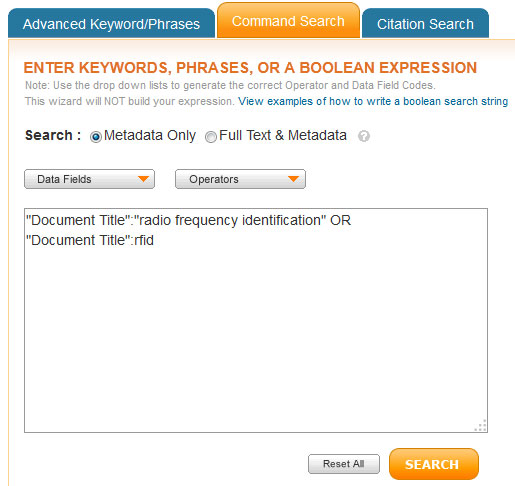
The Advanced Search Options page enables you to enter a free-form search query. In command search, you can specify and perform more complex searches than you can using structured advanced search. You can join up to 15 search terms, use proximity operators, and exert more control over the order in which expressions are evaluated.
To access the Command Search page, click on Advanced Search under the Global Search box and select the ![]() tab.
tab.
Data fields identify specific parts of a document record. By limiting a search to a specific field (or metadata), you can reduce the time it takes to process the search and produce more targeted results. Here are the data fields you can use in advanced search and/or command search.
Note: In Command Search, remember to enclose the field name in quotation marks, and use a colon to separate the field name from the field value you want to search for; for example, "Document Title":rfid.
| Abstract | Brief summary or statement of the contents of a journal article, conference paper, standard, book, book chapter, or course. |
| Accession Number | Sequential number assigned by INSPEC to each record or volume as it is added to the database. |
| Article Number | Unique record number assigned to an article. For example in the following URL, the article number is 5487489: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/freeabs_all.jsp?arnumber=5487489 |
| Author Affiliation | Institutional affiliation (university, government agency, corporation, etc.) of the first author listed in the article. |
| Author Keywords | Terms provided by the author which describe the topics or subjects of the document. |
| Authors | Name of the author or authors listed in the document. |
| Document Title | Title of an individual document (journal article, conference paper, standard, eBook chapter, or course). |
| DOI | Digital Object Identifier. A unique character string to identify an individual object such as a journal article or conference paper. |
| Full Text & Metadata | Includes the full-text of a document as well as all of the other fields. |
| IEEE Terms | Keywords assigned to IEEE journal articles and conference papers from a controlled vocabulary created by the IEEE. |
| Index Terms | Combined field which allows users to search the Author Keywords, DOE Terms, IEEE Terms, INSPEC Terms, Mesh Terms, and PACS Terms. |
| INSPEC Controlled Terms | Keywords assigned to articles from a controlled vocabulary of over 10,000 scientific terms created by INSPEC. |
| INSPEC Non-controlled Terms | Additional keywords assigned to articles which describe the topics or subjects of a document. These terms are not part of the INSPEC controlled vocabulary and include new and emerging concepts. |
| ISBN | International Standard Book Number. A number used to uniquely identify a book or non-serial. |
| ISSN | International Standard Serial Number. An 8-digit number used to uniquely identify a periodical publication (journal or serial). |
| Issue | Number of the journal issue in which the article was published. |
| Metadata | Includes the abstract, index terms, and bibliographic citation data (such as document title, publication title, author, etc.). |
| MeSH Terms | Medical Subject Headings defined by the National Library of Medicine (NLM). MeSH terms are integrated into IEEE Xplore for 14 IEEE biomedical-related titles. |
| Parent Publication Number | Number for the parent publication. This can be used to locate articles within a serial conference. |
| Publication Number | Unique record number assigned to a publication. For example in the following URL which links to the publication home page for IEEE Security & Privacy, the publication number is 8013: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/RecentIssue.jsp?punumber=8013 |
| Publication Title | Title of a publication (journal, conference, or book). |
| Standard Number | Standard designation (e.g., IEEE 802.11u-2011). Standard designations are allocated by the Administrator of the IEEE-SA Standards Board New Standards Committee (NesCom). |
| Standard Dictionary Terms | Terms included in the glossary of a standard and the IEEE Standards Dictionary. |
| Topic | One of the 16 topics listed in the By Topic menu under Browse (Aerospace, Bioengineering, etc). Topic names do not have to be exact. For example, entering computing as the field value will find all documents under the topic Computing & Processing (Hardware/Software). |
Search operators are elements that express relationships between search terms or search expressions, or that otherwise modify a query. In structured advanced searching, you can use the logical operators AND, OR, and NOT. In command searching, you can use these operators plus NEAR (for unordered proximity searches) and ONEAR (for ordered proximity searches), as described here.
| Operator | Syntax | Find Results That... |
| AND | x AND y |
Match both expressions x and y Example: "wireless sensor network" AND security Finds articles with both the phrase wireless sensor network and the word security |
| OR | x OR y |
Match either expression x or y or both Example: REV OR "renewable energy vehicle" Finds articles with either the word REV or the phrase renewable energy vehicle |
| NOT | NOT x | Do not match expression x |
| x NOT y |
Match expression x but not y Example: gasoline NOT diesel Finds articles that include the word gasoline but that do not include the word diesel |
|
| NEAR | x NEAR/# y |
Match expression x within # words of y (x can appear before or after y) Example: implantable NEAR/3 cardiac Finds articles with the word implantable within three words of cardiac; cardiac can come before or after implantable |
| ONEAR | x ONEAR /# y |
Match expression x before and within # words of y Example: implantable ONEAR/3 cardiac Finds articles with the word implantable within three words of cardiac; but implantable must come before cardiac |